1 Embryology
This chapter aims to give you sufficient insight into development to account for the arrangement of structures in the mature nervous system. If not already familiar with adult brain anatomy, we suggest you read this chapter again following study of Chapters 2 and 3.
Spinal Cord
Neurulation
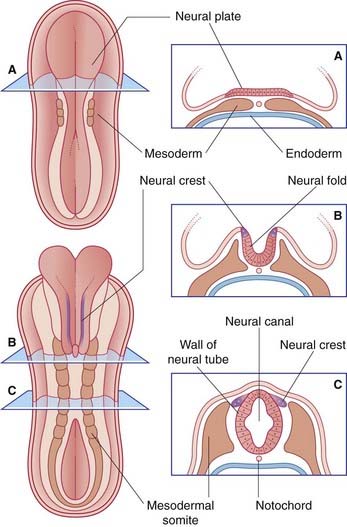
The entire nervous system originates from the neural plate, an ectodermal thickening in the floor of the amniotic sac (Figure 1.1). During the third week after fertilization, the plate forms paired neural folds, which unite to create the neural tube and neural canal. Union of the folds commences in the future neck region of the embryo and proceeds rostrally and caudally from there. The open ends of the tube, the neuropores, are closed off before the end of the fourth week. The process of formation of the neural tube from the ectoderm is known as neurulation.
Spinal nerves
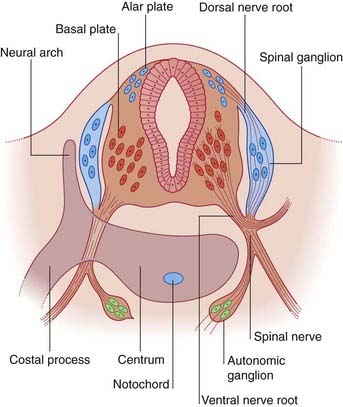
The dorsal part of the neural tube is called the alar plate; the ventral part is the basal plate (Figure 1.2). Neurons developing in the alar plate are predominantly sensory in function and receive dorsal nerve roots growing in from the spinal ganglia. Neurons in the basal plate are predominantly motor and give rise to ventral nerve roots. At appropriate levels of the spinal cord, the ventral roots also contain autonomic fibers. The dorsal and ventral roots unite to form the spinal nerves, which emerge from the vertebral canal in the interval between the neural arches being formed by the mesenchymal vertebrae.
Brain
Brain parts
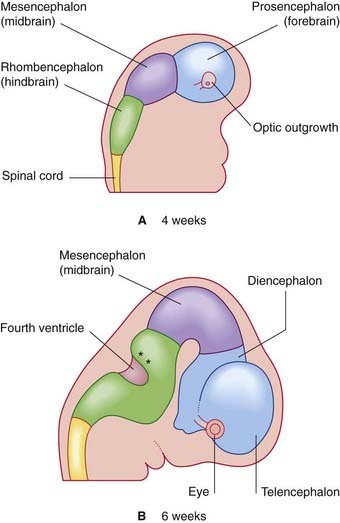
Late in the fourth week, the rostral part of the neural tube undergoes flexion at the level of the future midbrain (Figure 1.3A). This region is the mesencephalon; slight constrictions mark its junction with the prosencephalon (future forebrain) and rhombencephalon (future hindbrain).
The alar plate of the prosencephalon expands on each side (Figure 1.3A) to form the telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres). The basal plate remains in place here as the diencephalon. Finally, an optic outgrowth from the diencephalon is the forerunner of the retina and optic nerve.
The diencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon constitute the embryonic brainstem.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree