Extradural Lesion, T2 Hypointense, T1 Hypointense
Bryson Borg, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Intervertebral Disc Herniation
Endplate Osteophyte
Facet Osteophyte
Ossification Ligamentum Flavum
OPLL
Epidural Gas
Metal Artifact
Rare but Important
Epidural AVF
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Intervertebral Disc Herniation
Most common epidural lesion in adult population
Intermediate-to-low T1 signal
Variable T2 signal, hyperintense signal can be seen with annular fissures and sequestrations
Endplate Osteophyte
Endplate osteophyte formation commonly accompanies degenerative disc disease
May be difficult to distinguish osteophyte from a disc herniation on MR; NECT can supplement evaluation
Ossification Ligamentum Flavum
Enlargement of ligamentum flavum causing variable posterolateral encroachment on the thecal sac
Best conspicuity of calcifications on NECT
If sufficiently ossified, may produce marrow space with hyperintensity on T1WI
Idiopathic, probably related to hydroxyapatite or calcium pyrophosphate deposition
May observe changes of DISH or OPLL elsewhere in spine
OPLL
Idiopathic condition, resulting in calcification and thickening of the posterior longitudinal ligament
Most common in the cervical spine, can involve upper thoracic
Variable encroachment on the ventral spinal canal
If sufficiently ossified, may produce a marrow space with hyperintensity on T1WI
Epidural Gas
Routinely seen in the acute post-operative period
Can occur from
“Vacuum” disc phenomenon extending into disc herniation
“Vacuum” joint phenomenon extending into facet synovial cyst
Metal Artifact
Epidural catheters
Spinal cord stimulators
Spinal fusion hardware
Displaced intervertebral devices
Image Gallery
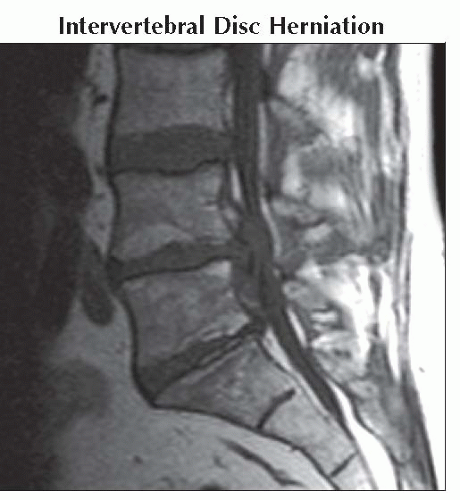 Sagittal T1WI MR shows a large disc extrusion at L4-5. Extruded disc material is similar in signal to the remainder of the intervertebral disc on T1WI.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|