A key pathologic feature characteristic of ALS neurons is the presence of intracytoplasmic deposits of ubiquinated immunoreactive inclusions, recently shown to be the protein TDP-43, a nuclear factor about which little is known.6,7 In normal neurons, it is localized in the nucleus; in sporadic ALS, it is mislocalized to the cytoplasm, where it deposits as dense round inclusions or as skein-like striations.
This patient’s clinical course and subsequent post mortem examination, including the demonstration of TDP-43 intracytoplasmic deposits (Fig. 37-1) confirm her diagnosis.
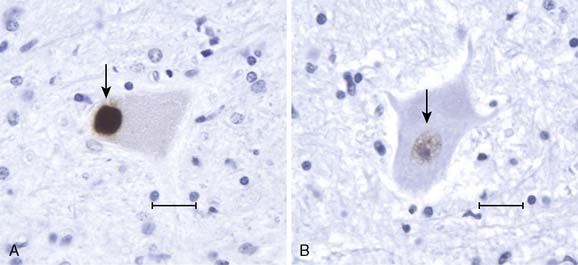
Figure 37-1 TDP-43 immunohistochemistry in spinal motor neurons. A, Patient. This lumbar motor neuron from the patient shows the intracytoplasmic dense round inclusion of TDP-43 (arrow) that is characteristic of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. B, Control. This is a normal lumbar motor neuron from a control patient to show by comparison the normal intranuclear distribution of TDP-43 (arrow). (Scale bar = 50 μm).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








