Fig. 5.1
Extrel type DBS system. (a) External transmitter (model 3523). (b) Antenna. (c) Receiver (model 3360). (d) Stimulation electrode (Reprinted with the permission of Medtronic, Inc. © 1991)
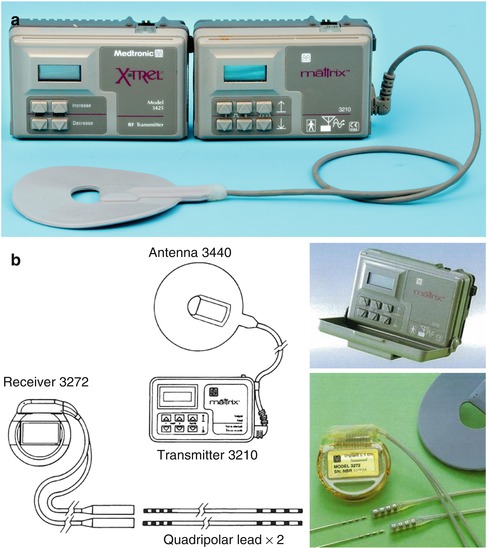
Fig. 5.2
(a) Extrel type transmitter. One channel (left) and two channel (right) transmitter. (b) Two channel Extrel type stimulation system (Reprinted with the permission of Medtronic, Inc. © 1994, 1996)
Later, the Itrel type DBS system was developed. The Itrel type DBS system consists of an implantable pulse generator (IPG) which contains its own battery, extension cable, and stimulation electrode. Thus, the DBS system became completely internalized. The patient receiving the DBS was no longer inconvenienced by the need to wear an external device. Recently, the IPG was developed further, such that one of the new IPG devices contains a rechargeable battery. The rechargeable battery is useful for the prolongation of battery life and has extended the time before IPG replacement is required up to 9 years.
5.2 DBS and MCS Electrode
The early DBS electrodes were quite different from the present DBS electrodes. There were four stimulation points as with recent electrodes, but the most distal stimulation point was ring shaped and the body of electrode was twisted as shown in Fig. 5.3. For the implantation of this electrode, the most distal ring-shaped part was hooked by a pointed guide needle and advanced toward the target. After that procedure, the guide needle was pulled out slowly so as not to move the tip of the implanted electrode.
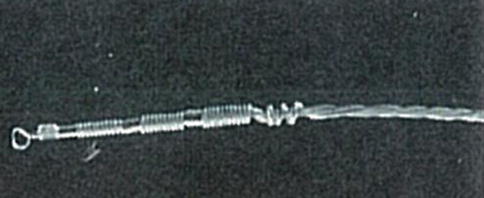

Fig. 5.3
The early DBS electrode (model 3380). This platinum–iridium electrode is composed of a distal loop and three other active contact points, each approximately 2-mm long
The present DBS electrode is also quadripolar, but the surface of the electrode is smooth and the tip of electrode is domelike in shape. This coaxial electrode has a central stylet, and the central stylet is pulled out after the electrode is advanced toward the target. Two types of DBS electrode (models 3387 and 3389, Medtronic Co, Minneapolis, USA) are commonly used, and both have a 1.27-mm diameter. Each individual contact is 1.5-mm high, and the difference between the two models is the spacing between the contacts. The contact edge-to-edge space is 1.5 mm in the model 3387 and 0.5 mm in model 3389. Therefore, the distances from the tip of the most distal contact point to the top of the most proximal contact point for these two electrode models are 10.5 and 7.5 mm, respectively (Fig. 5.4). The design of these DBS electrodes is shown in Fig. 5.5, and the device specifications for the leads are presented in Table 5.1. In addition, other DBS electrodes such as the Medtronic model 3387 IES (diameter, 1.27 mm; contact length, 3 mm; inter-electrode spacing, 4 mm) and model 3887 (diameter, 1.3 mm; contact length, 3 mm; inter-electrode spacing, 4 mm) have been developed to cover relatively wider target areas such as the anterior limb of the internal capsule for the treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder.
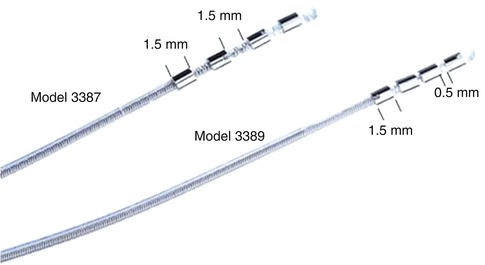
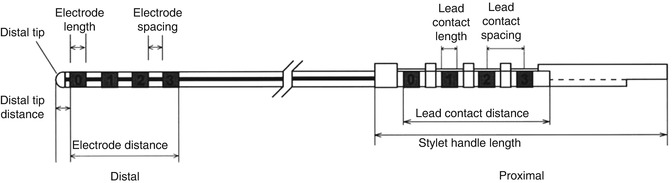

Fig. 5.4
The recent DBS electrodes. The Medtronic 3387 model has 1.5-mm contact spacing and the 3389 model has 0.5-mm spacing. Each individual contact is 1.5-mm high. Both electrodes are quadripolar and have a 1.27-mm diameter (Reprinted with the permission of Medtronic, Inc. © 2012)

Fig. 5.5
The design of recent DBS electrode (electrode, lead contact, and stylet) (Reprinted with the permission of Medtronic, Inc.)
Table 5.1
The device specifications for recent DBS electrodes 3387 and 3389
Description | Model 3387 | Model 3389 |
|---|---|---|
Connector | Quadripolar, in-line | Quadripolar, in-line |
Shape | Straight | Straight |
Conductor resistancea | <100 Ω | <100 Ω |
Length | 10–50 cm | 10–50 cm |
Diameter | 1.27 mm | 1.27 mm |
Distal end | ||
Number of electrodes | 4 | 4 |
Electrode shape | Cylindrical | Cylindrical |
Electrode length | 1.5 mm | 1.5 mm |
Electrode spacing | 1.5 mm | 0.5 mm |
Electrode distance | 10.5 mm | 7.5 mm |
Distal tip distance | 1.5 mm | 1.5 mm |
Proximal end | ||
Lead contact length | 2.3 mm | 2.3 mm |
Lead contact spacing | 4.3 mm | 4.3 mm |
Lead contact distance | 16.6 mm | 16.6 mm |
Stylet handle length | 40.1 mm | 40.1 mm |
The DBS electrodes are fixed into place with a combination of a plastic burr-hole ring and burr-hole cap contained in the DBS electrode package made by Medtronic Co. The burr-hole ring has a slit with a width of several mm, and small ring holes are located bilaterally beside the slit. It is possible to make the slit smaller by closing the bilateral small ring holes using pointed forceps, temporarily decreasing the diameter for placement into the perforated burr hole; once in place, the ring is released and expands in diameter to fix tightly to the burr-hole edge in the skull bone. The burr-hole ring also contains two grooves, which serve to fix the DBS electrodes. After that, the burr-hole cap is fixed to the burr-hole ring. The DBS electrodes are fixed in the groove of burr-hole ring and covered by the burr-hole cap (Yamamoto et al. 2003) (Fig. 5.6).
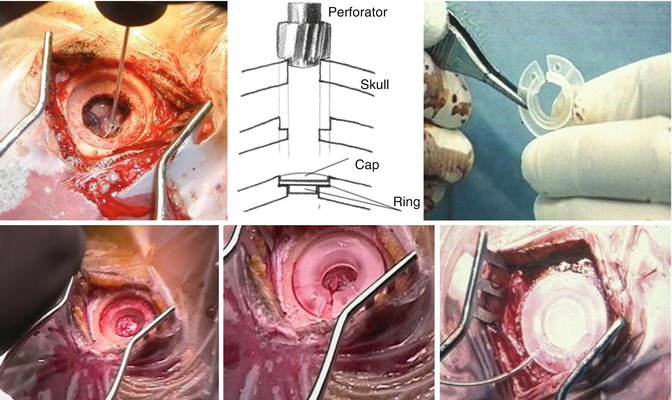

Fig. 5.6
Burr-hole ring and burr-hole cap. The DBS electrode is fixed by the burr-hole ring and burr-hole cap. We have also reported the dual floor burr-hole method, which is convenient for fixation (Yamamoto et al. 2003)
Tsubokawa et al. (1991) first applied MCS for poststroke pain and used the RESUME II electrode (Medtronic Co, Minneapolis, USA). The RESUME II electrode is a paddle type, single quadripolar column (1 × 4) electrode (Fig. 5.7). Recently, many more kinds of paddle-type electrodes have been developed, with different numbers of contact points (4–20 points) and columns (1–5), and different length and width paddles (Fig. 5.7).
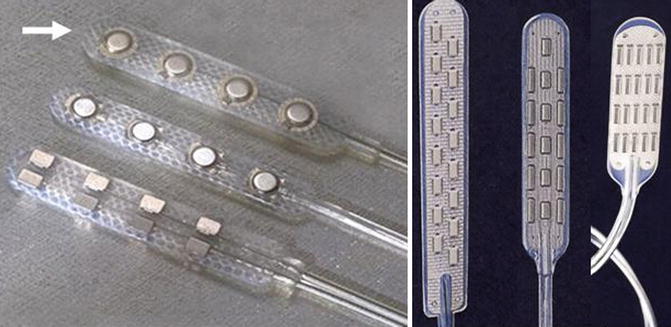

Fig. 5.7
The RESUME II electrode and other paddle type electrodes. RESUME electrode is a paddle type consisting of a single quadripolar column (1 × 4) electrode. The diameter of each stimulation point is 4 mm, and each stimulation point is separated by 6.2 mm (→). The number of contact points (4–20 points) and columns (1–5), and the length and width of the paddle are different in each electrode
5.3 Implantable Pulse Generator
In recent years, the Extrel type stimulation system, consisting of an external pulse generator, an antenna, and a receiver which contains the transmitter has become clinically obsolete. The Itrel type pulse generator, which is totally implanted and powered by an internal battery, is now the clinical standard. In an Itrel type pulse generator, both nonrechargeable and rechargeable pulse generators are available for clinical use. The rechargeable pulse generator must be periodically recharged with an external radiofrequency antenna, and the advantage of this system is longer duration of the batteries (up to 9 years) without need for replacement. At present, Medtronic Co. has released four types of IPGs for clinical use, namely, the Activa-PC-3761, Activa-RC-37612, Activa-SC-37602, and Activa-SC-37603. The Activa-PC-3761 and Activa-RC-37612 are multiprogrammable devices that deliver stimulation through one or two leads while Activa-SC-37602 and Activa-SC-37603 are multiprogram devices that deliver stimulation through only one lead. Only Activa-RC-37612 is a rechargeable type IPG, and the other three types are nonrechargeable type IPGs.
5.3.1 Activa® PC (Activa-PC-37601)
The Activa PC neurostimulator is a multiprogrammable device that delivers stimulation through one or two leads. The stimulation settings are stored as “programs” with specific pulse width, pulse rate, and pulse amplitude settings acting on a specific combination of electrodes. Up to four programs can be combined into a group. When using more than one program, the pulses are delivered sequentially—first a pulse from one program, then a pulse from the next program. Pulse width, amplitude, and electrode polarity for each program within the group can have different values. Rate, rate limits, SoftStart/Stop, and cycling for each program within the group have the same values (Fig. 5.8 and Table 5.2).
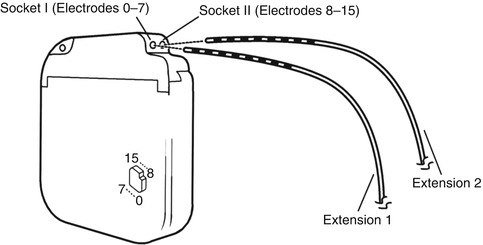

Fig. 5.8
Figure of Activa® PC (Activa-PC-37601) with connection to the stimulating electrode (Reprinted with the permission of Medtronic, Inc. © 2012)
Table 5.2
Device specifications for Activa® PC (Activa-PC-37601)
Description | Value |
|---|---|
Connector type | Octapolar, in-line 2.8 mm (0.110 in.) spacing |
Height | 65.0 mm (2.6 in.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|




