Intervertebral Disc, T2 Hyperintense
Jeffrey S. Ross, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Normal Variant
Degenerative Disc Disease
Vertebral Disc Anular Tear
Post-Operative Change, Normal
Post-Traumatic
Disc Space Infection
Less Common
Pseudoarthrosis
Neurogenic (Charcot) Arthropathy
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathy
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Normal Variant
Central disc shows biconvex central high signal
Horizontal low signal extends through nucleus giving bisaucer shape
Loss of central signal with disc degeneration
Degenerative Disc Disease
Typical decreased signal of intervertebral disc on T2WI
May show linear T2 hyperintensity with fluid-filled cleft in disc
Uncommon discal cysts along posterior margin
No paravertebral or epidural mass to suggest infection
Vertebral Disc Anular Tear
Focal increased signal in anulus on T2WI with low signal of parent disc
T1 C+: Focally enhancing nidus in posterior disc margin
Discography demonstrates contrast leak from central site of injection through anulus
Discography is more provocative test (symptom simulation) than diagnostic imaging modality
Post-Operative Change, Normal
Disc intervention may lead to increased fluid and T2 hyperintensity
Nonspecific post-operative change
Post-Traumatic
↑ T2 signal suggests disc disruption
Look for disruption of ALL, PLL
Disc Space Infection
Abnormal disc ↑ T2 with abnormal morphology hallmark of disc space infection
2 adjacent vertebrae involved with endplate irregularity and intervening disc abnormality
Paraspinal ± epidural infiltrative soft tissue ± loculated fluid collection
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Neurogenic (Charcot) Arthropathy
Irregular disc space fluid, facet involvement, spondylolisthesis, debris, disorganization
Image Gallery
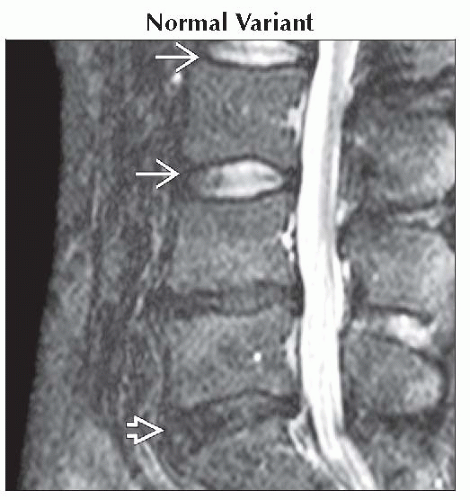 Sagittal T2WI MR shows normal hyperintensity of L2-3, L3-4 discs
 with horizontal central low signal (intranuclear cleft). There is degeneration and loss of signal of L4-5, L5-S1 with horizontal central low signal (intranuclear cleft). There is degeneration and loss of signal of L4-5, L5-S1  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|