Intradural/Extramedullary Lesion, T1 Hypo, T2 Hypo
Jeffrey S. Ross, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
CSF Flow Artifact
Post-Operative Change, Normal
Metal Artifact
Vascular Malformation
Meningioma, Calcified
Less Common
Ependymoma, Myxopapillary (Calcified)
Arachnoiditis Ossificans
Superficial Siderosis
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
CSF Flow Artifact
Related to both time-of-flight (TOF) effects and turbulent flow
Turbulent flow ⇒ more rapid dephasing with signal loss
TOF signal loss seen with SE or FSE when protons do not experience both initial RF pulse and subsequent refocusing pulse
Increased signal loss with higher flow velocity, thin slices, longer TE, imaging perpendicular to flow
Gradient echo imaging less susceptible to CSF flow artifacts
Repeat study with different imaging plane, GE sequences with short TE
Post-Operative Change, Normal
Most common will be small foci of gas from violation of dura
Metal Artifact
Fast spin echo better than conventional spin echo better than gradient echo
Use larger field of view
Appropriate geometric orientation of frequency encode direction
Parallel to pedicle screws
Vascular Malformation
Most common is type 1 dural fistula
Hallmark is T2 hyperintense cord (usually distal thoracic), intradural flow voids (especially dorsal)
Meningioma, Calcified
Well-defined ID/EM lesion with dural base
Generally low T2 signal
Solitary lesion, except with NF2
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Ependymoma, Myxopapillary (Calcified)
Well-defined enhancing cauda equina mass with evidence of prior hemorrhage
Arachnoiditis Ossificans
Intradural ossification associated with post-inflammatory adhesion and clumping of lumbar nerve roots
Low signal thickened dura and roots
Superficial Siderosis
SAH (multiple etiologies) causing hemosiderin deposition on cord, nerve surface
Diffuse hypointensity of cord surface on T2WI, GE
Image Gallery
Nipple Structure
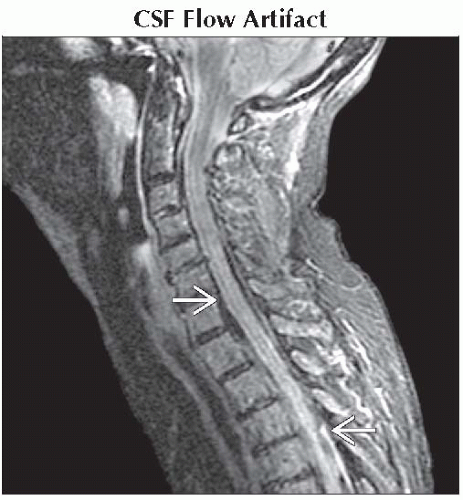 Sagittal STIR MR shows prominent signal loss involving the CSF throughout the cervical and upper thoracic spine
 related to CSF pulsation and flow dephasing. related to CSF pulsation and flow dephasing.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|