Intradural/Extramedullary Lesion, T2 Hyper, T1 Iso
Jeffrey S. Ross, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Schwannoma
Neurofibroma
Epidermoid
Ependymoma
CSF Disseminated Metastases
Less Common
Cysticercosis
Tuberculoma
Sarcoidosis
Meningioma
Rare but Important
Paraganglioma
Capillary Hemangioma
Neurenteric Cyst
Echinococcus
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Schwannoma
Well-circumscribed, dumbbell-shaped, enhancing spinal mass
30% of primary spine tumors
75% T2 hyperintense
Solitary unless part of inherited tumor syndrome, such as NF2
Scan entire spine in asymptomatic patients with suspected neurofibromatosis type 2
Neurofibroma
Bulky multilevel spinal nerve root tumors in patient with NF1
Rapid growth of NF suggestive of malignant transformation
Target sign suggestive of neurofibroma => peripheral high signal, central lower signal
Epidermoid
Nonenhancing intradural mass similar to CSF signal on T2/T1 images
Ependymoma
Myxopapillary type within caudal sac may show near iso T1 signal, T2 hyperintensity
Large fraction (20-30%) may show little enhancement
CSF Disseminated Metastases
Look for “dirty” CSF appearance on T1, with indistinct cauda and conus
Diffuse or nodular enhancement along cauda equina
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Capillary Hemangioma
Benign tumor of endothelial cell origin
T2 hyperintense enhancing well-defined intradural mass
May be indistinguishable from meningioma or schwannoma
Neurenteric Cyst
Intraspinal cyst and vertebral abnormalities
Osseous canal enlargement, widening of interpedicular distance
Iso- → hyperintense T1 reflecting protein/mucin content
Image Gallery
Nipple Structure
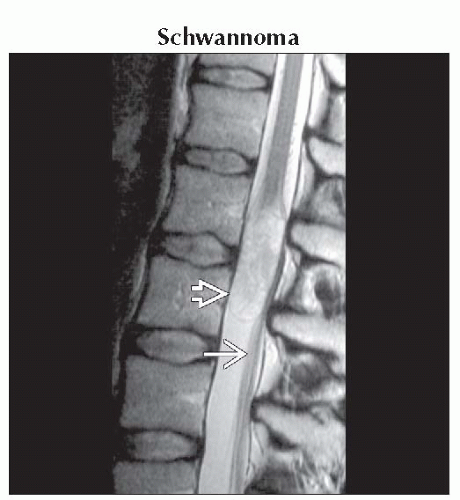 Sagittal T2WI MR shows a sharp margin of rounded schwannoma
 involving the cauda equina as a T2 hyperintense mass and displacing the roots of cauda posteriorly involving the cauda equina as a T2 hyperintense mass and displacing the roots of cauda posteriorly  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|