Intramedullary Lesion, T1 Hypointense, T2 Hypointense
Lubdha M. Shah, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Instrumentation/Implants
Contusion-Hematoma, Spinal Cord
Cavernous Malformation, Spinal Cord
Less Common
Cysticercosis
Type II AVM
Rare but Important
Diastematomyelia
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Assess for post-surgical changes
Flow voids suggest vascular lesion
Associated vertebral body anomalies in diastematomyelia
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Instrumentation/Implants
Intrathecal & epidural catheters allow infusion of anesthetics
Syringomyelia (hindbrain herniation or post-traumatic) treated with shunting into subarachnoid, peritoneal or pleural spaces
Complications: Infectious/inflammatory process, misplacement, cord or nerve injury, CSF leak, & spinal hematoma
Contusion-Hematoma, Spinal Cord
Acute contusion is T1 iso-/ hypointense
Blood products hypointense on T2 & T2* GRE sequences
± Cord swelling
Cavernous Malformation, Spinal Cord
T1 & T2 heterogeneous due to blood products of varying ages
T2 hypointense rim (hemosiderin)
No edema unless recent hemorrhage
No prominent vascular flow voids or nidus
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Cysticercosis
Focal cystic lesion(s) with or without syrinx cavity
T2 hypointensity may be due to cyst wall degeneration with calcification
Peripheral cyst enhancement
Type II AVM
Intramedullary nidus with dorsal subpial extension
Cord enlargement with heterogeneous T1/T2 signal due to blood products & flow voids
Intra-/perinodal aneurysm in 40%
Subarachnoid is most common symptom
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Diastematomyelia
Type 1 has separate dural sac & arachnoid space, more common
Iso-/hypointense spur (osseous or fibrous)
Type 2 has a single dural sac & arachnoid space
± Iso-/hypointense fibrous spur
Two hemicords with or without syringohydromyelia (50%)
Image Gallery
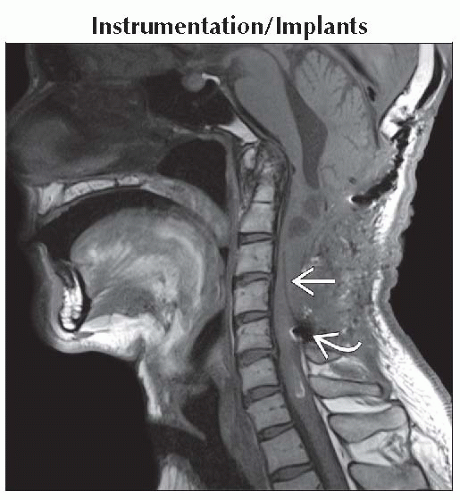 Sagittal T1WI MR shows a linear T1 hypointense catheter within the cervical syrinx cavity
 . Susceptibility artifact at the entry site of the catheter is also seen . Susceptibility artifact at the entry site of the catheter is also seen  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|