Figure 11-1 3-Tesla MRI of the lumbosacral plexus. Top: oblique coronal T2-weighted fast-spin echo sequence with fat saturation showing enlargement and prominent hyperintensity in the left sciatic nerve (long arrow), and mild to moderate hyperintensity in the right sciatic nerve (short arrow). Bottom: Postgadolinium oblique coronal T1-weighted spoiled recalled gradient sequence with fat saturation shows enhancement of the left sciatic nerve (arrow). Sciatic veins are marked with *.
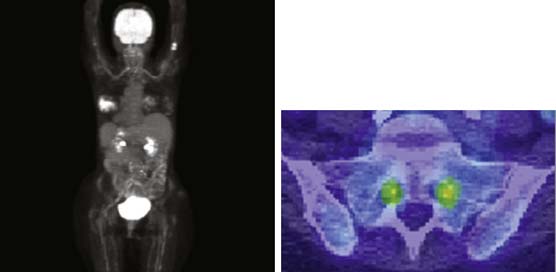
Figure 11-2 Fludeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) scan. Left: Reconstructed overview image of FDA uptake demonstrating increased activity within the left breast, proximal humeri, bilateral lumbosacral nerve roots, plexus and sciatic nerves, and mildly also bilateral brachial plexus. Right: PET/CT fusion of an axial cut through the spine at the level of the exiting S1 nerve roots. Note the increased activity of S1 nerve roots delineated in green and yellow.
A left sciatic fascicular nerve biopsy was performed and demonstrated moderately decreased density of myelinated fibers in a multifocal pattern, an increased rate of axonal degeneration, an increased rate of segmental demyelination, and an increased rate of empty nerve strands. There were large collections of mononuclear cells, many immature appearing, infiltrating the nerve and disrupting its architecture. The immunohistochemical profile was diagnostic of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with associated reactive inflammation (Fig. 11-3).
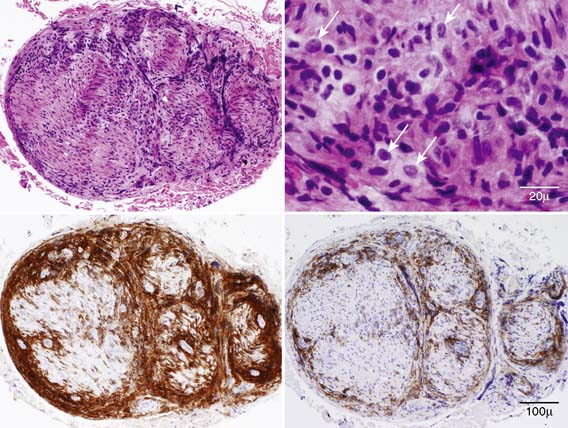
Figure 11-3 Fascicular biopsy of the left sciatic nerve. H&E (top), LCA (bottom left), and CD-20 immunostain (bottom right). Note abundant subperineurial and endoneurial mononuclear cells, infiltrating the nerve and disrupting its architecture. H&E stain at higher magnification (top right) shows large, atypical, immature appearing cells (arrows). The findings are diagnostic of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with associated reactive inflammation.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








