Autoimmune |
Primary demyelinating |
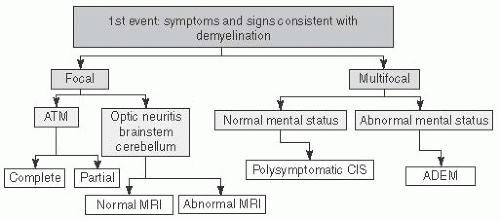
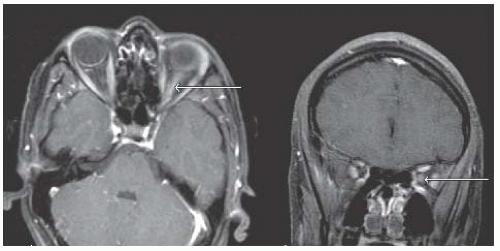
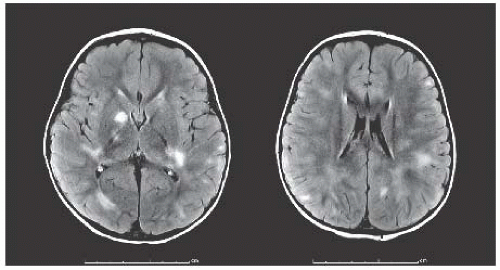
ON, ADEM, TM, CIS, MS (RRMS, SPMS, PPMS), NMO |
Paraneoplastic |
Paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis, OMS |
Connective tissue dz |
SLE, Behçet disease, RA, Sjögren syndrome, APLAS, HLH |
Granulomatous |
Wegener granulomatosis, sarcoidosis, lymphomatoid granulomatosis |
Vasculitis |
CNS and systemic vasculitides |
Other Demyelinating |
Infectious |
CMV, HIV → PML (JCV, usually in HIV), Lyme, neurosyphilis, HTLV1, SSPE, tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV1-assoc. myelopathy, congenital toxoplasmosis |
Metabolic |
CPM, subacute combined degeneration (B12 & intrinsic factor deficiency) |
Toxic |
NO poisoning; drugs of abuse (toluene, ethanol, cocaine, MDMA/ecstasy, IV/inhaled heroin, psilocybin); radiation-induced necrosis; anti-neoplastic agents (methotrexate, carmustine, cisplatin, cytarabine, fluorouracil, levamisole, fludarabine, thiotepa, interleukin-2, interferon-α); immunosuppressants (Cyclosporine [posterior lobes], tacrolimus [parieto-occipital]); antimicrobials (amphotericin B, hexachlorophene, metronidazole); environmental exposure (carbon monoxide, arsenic, carbon tetrachloride). |
Vascular & hypoxic-ischemic |
Migraine, PRES, HIE, sickle cell disease, delayed hypoxic cerebral demyelination, CADASIL |
Secondary demyelinating |
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy, metachromatic leukodystrophy, adrenomyeloneuropathy, Alexander, Canavan, Krabbe, Aicardi-Goutières syndrome |
Hypomyelinating |
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher, Cockayne syndrome |
Mitochondrial disease |
NARP, POLG1/Alpers, MELAS, Leigh syndrome |
Neoplasm |
Glioma, lymphoma, LCH |
Note: Most common in bold. |
ADEM, acute disseminated encephalomyelopathy; APLAS, antiphospholipid antibody syndrome; CADASIL, cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy; CIS, clinical isolated syndrome; CPM, central pontine myelinolysis; HIE, hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy; HLH, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome; JCV, JC virus; LCH, Langerhans cell histiocytosis; MELAS, multifocal encephalopathy lactic acidosis and strokes; MS, multiple sclerosis; NARP, neuropathy ataxia and retinitis pigmentosa; NMO, neuromyelitis optica; NO, nitric oxide; OMS, opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome; ON, optic neuritis; PML, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy; POLG1, polymerase gamma 1; PPMS, persistently progressive MS; PRES, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; RRMS, rapidly progressive MS; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SPMS, secondary progressive MS; SSPE, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis; TM, transverse myelitis. |
|