Subarachnoid Space Narrowing
Bryson Borg, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Stenosis, Acquired Spinal
Stenosis, Congenital Spinal
Extra-axial Mass
Hematoma, Epidural-Subdural
Abscess, Epidural
Meningioma
Metastasis, Epidural
OPLL
Enlarged Cord
Demyelinating Disease
Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord (Acute)
ADEM, Spinal Cord
Acute Transverse Myelitis, Idiopathic
Neuromyelitis Optica
Syringomyelia
Ependymoma, Cellular, Spinal Cord
Astrocytoma, Spinal Cord
Metastases, Spinal Cord
Radiation Myelopathy
Less Common
Arachnoiditis, Lumbar
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Stenosis, Acquired Spinal
Multifactorial process involving disc herniation and degenerative hypertrophy of the posterior elements
Stenosis, Congenital Spinal
Developmentally narrow canal; short, thick pedicles
Frequency: Lumbar > cervical > thoracic
Hematoma, Epidural-Subdural
May be spontaneous or associated with trauma or instrumentation
Signal varies with the age of the hemorrhage
Mild or no enhancement
Abscess, Epidural
May be associated with disc space infection or instrumentation/inoculation
Marked peripheral enhancement typical
Meningioma
Dural-based, circumscribed, enhancing mass
Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord (Acute)
Cord expansion uncommon, indicates an acute lesion; resolves in 6-8 weeks
Hyperintense on T2WI, variable enhancement
Image brain to check for supratentorial lesion(s)
Ependymoma, Cellular, Spinal Cord
Circumscribed, enhancing intramedullary mass
Necrosis and hemorrhage possible
Astrocytoma, Spinal Cord
Fusiform enlargement, infiltrative margins; no or variable enhancement
Imaging cannot reliably differentiate from ependymoma
Appearance can be simulated by acute MS, ADEM, neuromyelitis optica, myelitis
Image Gallery
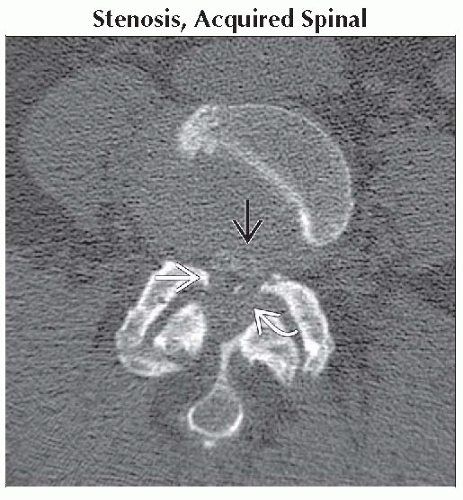 Axial CECT (CT myelogram) shows almost complete loss of the CSF spaces within the thecal sac
 due to protruding disc, facet arthropathy due to protruding disc, facet arthropathy  , and ligamentous hypertrophy , and ligamentous hypertrophy 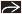 . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|