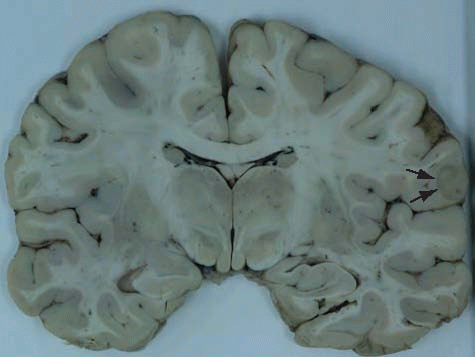
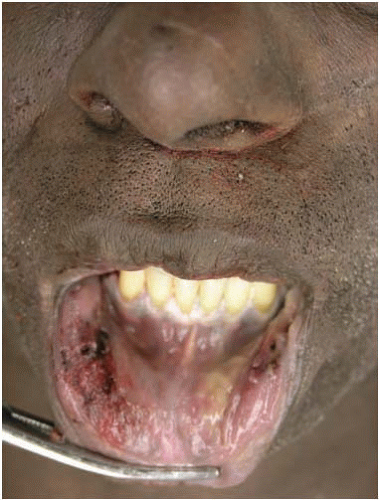
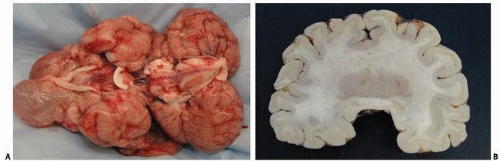
vehicle, or industrial mishaps, which are more common among epileptics than in the general population.22, 23 The classical scenario in accidental deaths in epilepsy is when an individual with a history of seizures is witnessed to have a seizure, and the resultant erratic driving causes an accident. At other times, epileptics may drown, and the logical inference is that they suffered a seizure that resulted in drowning. Further, seizures causing an accident may be the most likely explanation for death in cases with or without a history of seizures, when a seizure focus is identified at autopsy and no other cause of death or any other explanation for the accident is apparent, as in Case 14.1.
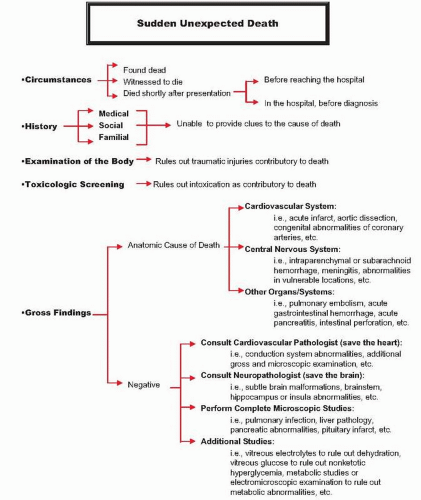 FIG. 14.1. Schematic representation of the algorithm followed in the work-up of sudden deaths at the Office of the Chief Medical Examiner of the State of Maryland. |
done, the autopsy results are not complete, or the autopsy is suboptimal because the body is decomposed), cases may be categorized as probable SUDEP.
|
TABLE 14.1 Age and Sex Comparison of Adult Individuals with Natural Death from All Causes and Those with CNS-Related Natural Death: 10-Year Review of Cases Studied at the Office of the Chief Medical Examiner of the State of Maryland (1997-2006) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
myocardium of SUDEP individuals than in controls. Vagal nerve stimulation procedure has been reported to produce a 40% reduction in seizures27, which may decrease the incidence of SUDEP in cases of intractable epilepsy. Pulmonary insufficiency in SUDEP can result from central apnea, obstructive compromise of the airways, or positional asphyxia related to the seizure episode itself.40 Experimental models of SUDEP have shown a decrease in blood oxygenation, hypercapnia, and metabolic acidosis in the post-ictal period.49 Pulmonary edema is a common finding in SUDEP and, on the basis of animal studies, 49 may be a sign of autonomic dysfunction.
TABLE 14.2 Cause of Death Distribution in Adult Natural Deaths of CNS-Related Pathogenesis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
the primary location of hemorrhage in ruptured berry aneurysms, but the blood sometimes dissects through the brain parenchyma and accumulates into the ventricular system or perforates the leptomeninges, producing a secondary subdural hematoma. Because the majority of extradural hematomas are traumatic in origin, we exclude them from the current discussion and limit this review to nontraumatic subarachnoid, subdural, intraparenchymal, and intraventricular hemorrhages, which are capable of producing sudden unexpected death in adults.
TABLE 14.3 Neuropathologic Findings in Sudden Unexplained Death in Epilepsy | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ruptured berry aneurysms presenting with sudden death and those that arrived alive to the hospital found that 38% of the aneurysms involved the posterior circulation in the first group and 14% in the second. A meta-analysis showed that the risk of sudden death in ruptured vertebrobasilar aneurysms was more than twice the risk for death in ruptured anterior circulation aneurysms.68, 70 Risk factors associated with aneurysmal rupture include female gender, middle age, smoking, and history of hypertension (albeit undiagnosed or untreated).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree