Vertebral Body Thickened Bony Trabeculae
Lubdha M. Shah, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
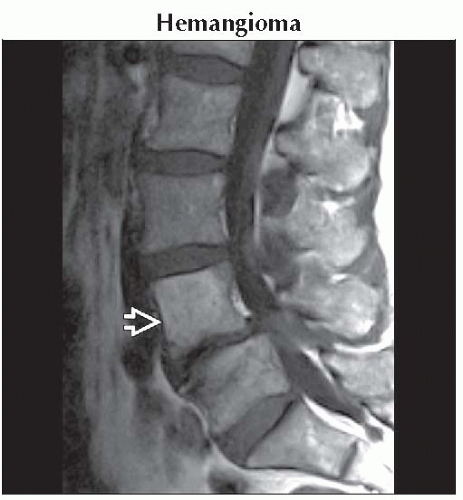
Hemangioma
Paget Disease
Osteoporosis
Less Common
Fibrous Dysplasia
Plasmacytoma
Rare but Important
Metastases, Blastic Osseous
Lymphoma
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Vertebral expansion in Paget disease, fibrous dysplasia, plasmacytoma
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Hemangioma
Corduroy pattern of thickened trabeculae & intervening fat
Aggressive lesions are characterized by epidural extent & cord compromise
T1/T2 hyperintense
Paget Disease
Coarsened & irregular bony trabecular pattern with cortical thickening
Heterogeneous, predominantly hypointense on T1 & hyperintense on T2
Vertebral expansion leads to varying degrees of spinal & neural foraminal stenosis
Osteoporosis
Marrow heterogeneity with focal islands of red marrow & centers of fat
Focal deposits of yellow marrow, esp. in posterior elements, around central venous channels, & adjacent to endplates
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Fibrous Dysplasia
Ground-glass matrix in mildly expanded lesion of the neural arch > vertebral body
Plasmacytoma
Originate in the vertebral body, although involvement of the posterior elements not uncommon
Endplate fractures produce curvilinear low signal areas &/or cortical irregularities
Thickened cortical struts in expanded vertebral body, “mini brain”
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Metastases, Blastic Osseous
Vertebral body, esp. posterior cortex, & pedicle are involved
Sclerotic lesions may be discrete & nodular, mottled, or diffusely increased density
Hypointense on T1WI & T2WI
Variable enhancement depending on degree of sclerosis
Lymphoma
Bony lymphomatous involvement results from hematogenous spread (95%)
Diffuse, mottled pattern with reduced signal on T1 & T2 sequences
Image Gallery