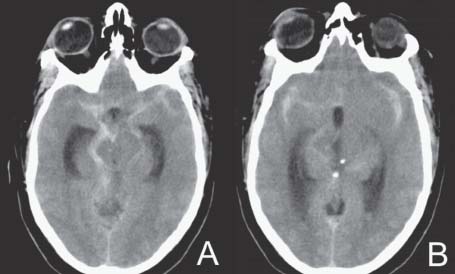
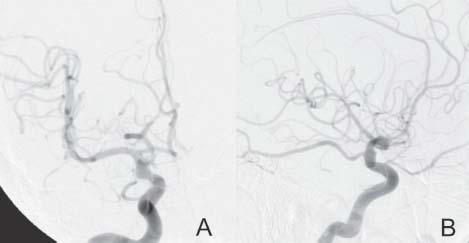
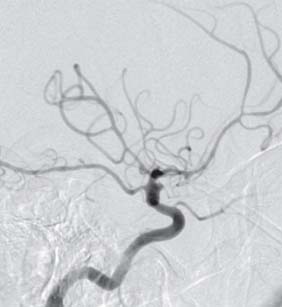
Case 34 Blister Carotid Aneurysm Fig. 34.1 (A,B) Computed tomography scan of the head showing a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Fig. 34.2 Cerebral angiography. (A) Anteroposterior and (B) lateral views of a right internal caro tid. Fig. 34.3 Cerebral angiography: Lateral view, right internal carotid done 3 days later.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Questions
Questions
 Answers
Answers
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
34 Blister Carotid Aneurysm
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


