Case 37 Hypertensive Putaminal Hematoma
Remi Nader
Fig. 37.1 Follow-up computed tomography scan without contrast at the level of the basal ganglia.
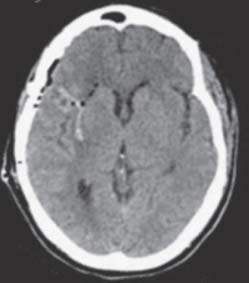
Fig. 37.2 Postoperative computed tomography scan without contrast at the same level of the basal ganglia.
- A 56-year-old woman with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and obesity presents with sudden-onset left-sided weakness.
- Initial studies show a 2-cm right-sided basal ganglia intracerebral hematoma (ICH).
- She is managed conservatively in the intensive care unit (ICU) initially; however, she starts becoming lethargic on day 5 and her weakness is more pronounced.
- A follow-up computed tomography (CT) scan is obtained (Fig. 37.1).
Fig. 37.3 Guidelines for the treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage. (GCS, Glasgow Coma Scale; ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage.) (Adapted from Mendelow AD, Gregson BA, Fernandes HM, et al. Early surgery versus initial conservative treatment in patients with spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral haematomas in the International Surgical Trial in Intracerebral Haemorrhage (STICH): a randomised trial. Lancet 2005;365:387–397; Broderick JP, Adams HP Jr, Barsan W, et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. A statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Stroke 1999;30:905–915.)
< div class='tao-gold-member'>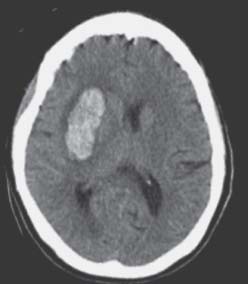
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation Questions
Questions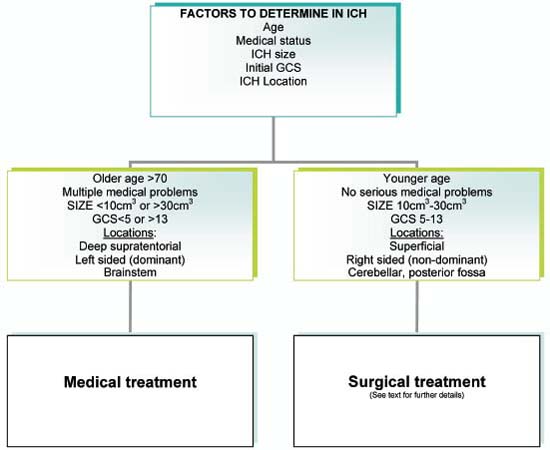
 Answers
Answers


