Fig. 61.1
Cavernous malformation (angioma). (a) Sagittal T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced MR image showing a multilocular lesion with high signal intensity surrounded by a rim with low signal intensity, continuing anteriorly along both optic nerves. (b, c) Coronal and axial views of gadolinium-enhanced images show mild enhancement of the mass (From Shibuya et al. [5]; with permission)
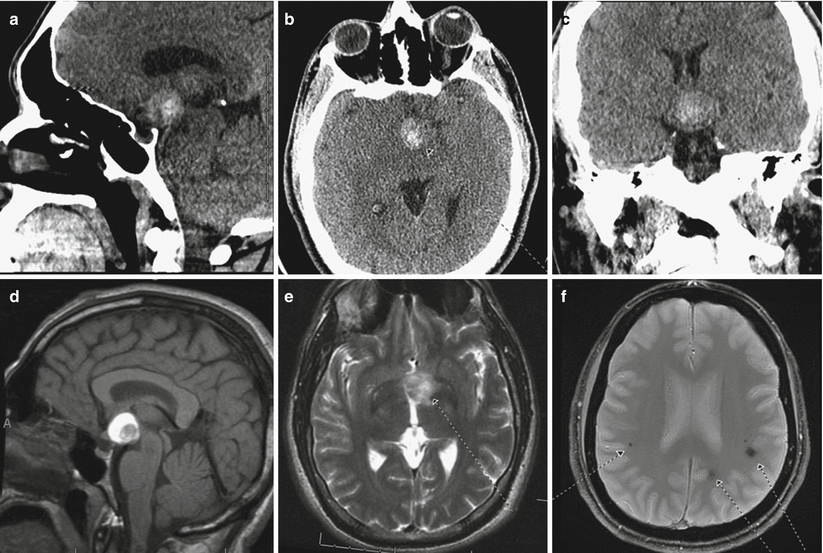
Fig. 61.2
Cavernous malformation (angioma). Sagittal (a), axial (b), and coronal (c) non-enhanced CT scans show a hyperdense mass in the suprasellar region. A sagittal T1-weighted non-enhanced MR image (d) demonstrates a predominantly T1-hyperintense mass in the suprasellar region at the level of the hypothalamus and tuber cinereum, abutting the distal basilar artery tip. Predominant signal characteristics are compatible with subacute methemoglobin. An internal nodular component demonstrates regional and circumferential low signals, which bloomed on gradient echo images compatible with hemosiderin at the site of the preexisting exophytic, hypothalamic cavernoma. An axial T2-weighted image (e) demonstrates a predominantly hyperintense signal compatible with extracellular methemoglobin within the 2-cm mass centered at the left paramedian, anteroinferior floor of the third ventricle. T2-weighted gradient echo images (f) demonstrate secondary areas of blooming signal void compatible with chronic hemosiderin deposition at sites of smaller cavernomas in the subcortical frontoparietal white matter and cervicomedullary junction (Adapted with permission from Rheinboldt and Blase [2])
Angiography is typically negative in patients with cavernous malformations.
Developmental venous anomalies (DVAs) may be seen in conjunction with cavernous malformations.
61.3 Histopathology
On gross examination, cavernous malformations are often well circumscribed, lobulated, and red/purple “mulberry”-like lesions.
Cavernous angiomas (malformations) are congenital intraparenchymal lesions with thin-lined capillaries that are lined by a single-layer endothelium, separated by collagenous stroma with no intervening brain parenchyma, and contain sinusoidal spaces. Intranidal hemorrhage and thrombosis are commonly seen.
61.4 Clinical and Surgical Management
Surgical treatment via craniotomy is recommended for most cases of symptomatic suprasellar cavernous malformations. Gross total resection is associated with improved visual outcomes [12].
A pterional or subfrontal cranial approach is typically utilized for surgical resection [13].
Emergent surgery is recommended for patients presenting with acute visual loss caused by chiasmal hemorrhage and/or apoplexy in the presence of a cavernous malformation [12, 14].
Indocyanine green has been used to help identify and confirm the resection of optic cavernous malformations, because the lesion typically will not be visualized following administration of indocyanine green, whereas the brain, optic chiasm/nerves, and small vessels are visualized [11].
The use of stereotactic radiosurgery for cavernous malformations is debated [15]. Radiosurgery has been reported to reduce the risk of rupture associated with cavernous malformations. In treating perioptic lesions in the suprasellar region, fractionated radiosurgery is typically required [16].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








