Fig. 41.1
Sellar region lymphoma. (a) Sagittal T1-weighted image. (b) Coronal T1-weighted image. There is nodular thickening of the pituitary stalk with diffuse enlargement of the gland
41.3 Histopathology
Sellar lymphoma represents large, B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in 54 % of cases [3, 5, 13] (Fig. 41.2).
Less frequently, sellar lymphoma can have a T-cell origin (24 % of cases), may be T-cell lymphoma with reactive B-cell lymphocytes or rarely may be the Burkitt’s variety [1, 4, 5, 14].
It is typically characterized by dense cellularity with a high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio.
B-cell varieties demonstrate positive immunostaining for CD20, CD79a and CD45 [3].
T-cell varieties are frequently positive for CD3, CD5, and CD8 immunostains.
The lymphoma may occur with concomitant hypophysitis [15].
There is generally a lack of immunoreactivity for hormonal cell markers.
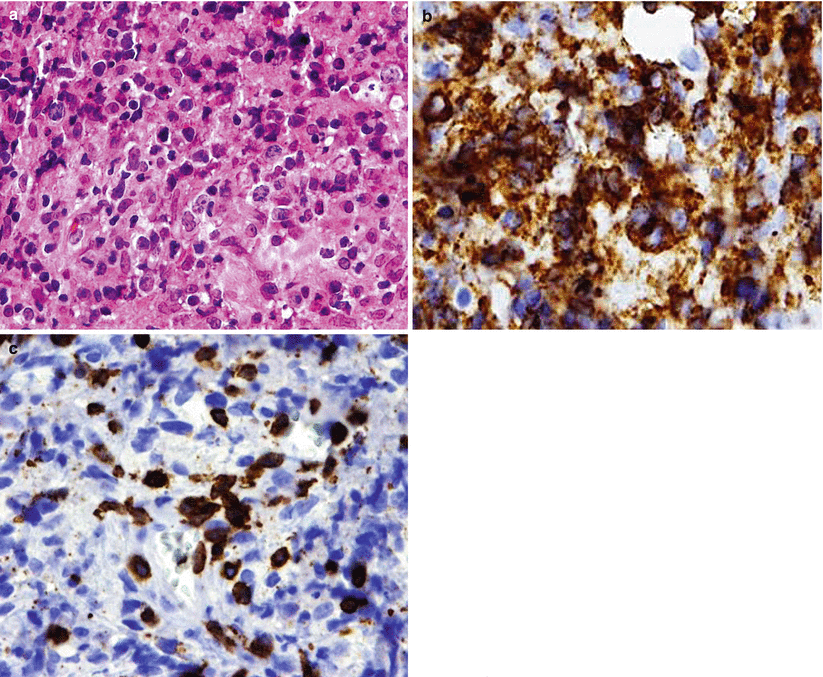
Fig. 41.2
Large B-cell lymphomas may involve the pituitary as primarily tumors or by secondary involvement of bone marrow disease. (a–c) In this case of a disseminated, diffuse, large B-cell lymphoma, the pituitary and the sellar soft tissues were invaded by a population of large cells with pleomorphic nuclei (a) immunoreactive for CD20 (b); small, reactive T cells may be present, as demonstrated by CD3 (c)
41.4 Clinical and Surgical Management
The role of surgery is primarily biopsy and perhaps partial tumor debulking, especially in patients with visual loss [5].
Radiation and chemotherapy are the mainstays of treatment.
On average, survival is increased from 4 months with surgery alone to 12–18 months with whole-brain radiotherapy [17].
The most common chemotherapy regimens include high-dose methotrexate and cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP), followed by whole-brain radiotherapy [18, 19].
Approximately 70 % of examined patients with primary pituitary lymphoma survive more than 6 months after diagnosis, whereas survival is often less than 6 months for patients with cerebral lymphomas [5].
References
1.
2.
Da Silva AN, Lopes MB, Schiff D. Rare pathological variants and presentations of primary central nervous system lymphomas. Neurosurg Focus. 2006;21(5), E7.CrossRefPubMed
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








