Fig. 24.1
Petrous apex cholesterol granuloma. (a) Axial CT image with contrast enhancement. (b) Coronal CT image with contrast enhancement. (c) Axial T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced image. (d) Coronal T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced image. There is an ovoid cystic lesion in the right petrous apex, containing predominantly T1-hyperintense material. The right internal carotid artery is displaced anteriorly
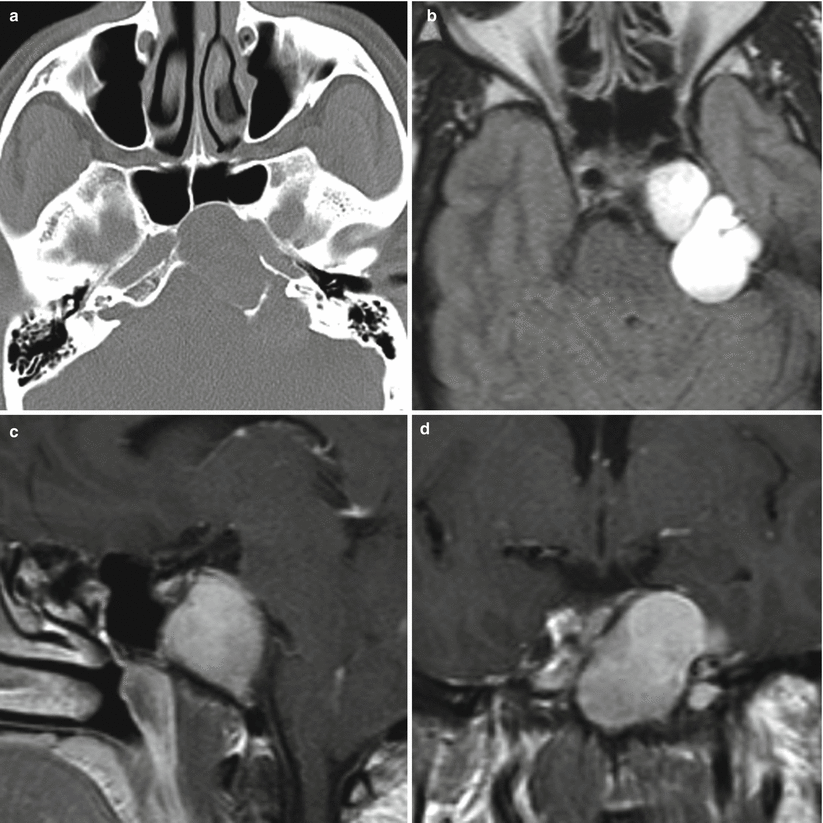
Fig. 24.2
Petrous apex cholesterol granuloma. (a) Axial CT image with contrast enhancement. (b) Axial FLAIR image. (c) Sagittal T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced image. (d) Coronal T1-weighted gadolinium-enhanced image. There is an expansile cystic lesion in the left petrous apex containing T1-hyperintense material. The cyst expanded to the clivus body with anterior displacement of the left cavernous internal carotid artery. Posteriorly, the cyst indents the brainstem
24.3 Histopathology
Chocolate-colored fluid contents are often grossly observed.
Petrous apex cholesterol granulomas are characterized by cholesterol clefts surrounded by histiocytes, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and multinucleated foreign-body giant cells [9].
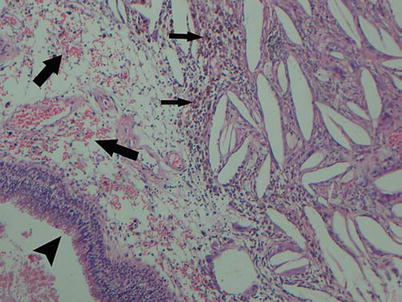
Fig. 24.3
In a petrous apex cholesterol granuloma, a large number of submucosal spindle-shaped, empty clefts surrounded by inflammatory cells are shown. The intact respiratory epithelium is noted (arrowhead). Focal hemorrhage (large arrows) and hemosiderin-laden macrophages (small arrows) are also shown (H&E stain, ×100) (Adapted from Chao [10]; with permission)
24.4 Clinical Management
Surgical management is the preferred primary treatment for symptomatic petrous apex cholesterol granulomas.
Open surgical approaches such as a middle cranial fossa or infracochlear approach have been traditionally used [11].
Endoscopic endonasal approaches for selected cholesterol granulomas offer the potential for effective and safe marsupialization and drainage [12].
Symptomatic improvement, including resolution of cranial nerve deficits, has been reported in 80–100 % of patients [12, 13].
A primary surgical goal is to establish a long-standing drainage route, such as into the sphenoid sinus.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








