Fig. 68.1
Pituitary hypoplasia. (a) Sagittal T1-weighted precontrast MR image. (b) Coronal T1-weighted precontrast image. The anterior pituitary gland is hypoplastic and the posterior pituitary T1 shortening is visible in the center of the sella. The stalk is present
The height of a hypoplastic pituitary gland, when present, is typically less than 3 mm; the normal height is more than 5 mm [8].
An ectopic pituitary gland may be visualized [21].
In patients with congenital GH deficiency, the triad of an ectopic posterior pituitary (EPP), pituitary aplasia/hypoplasia, and stalk defects is correlated with the presence of other endocrine abnormalities (Fig. 68.2) [22].
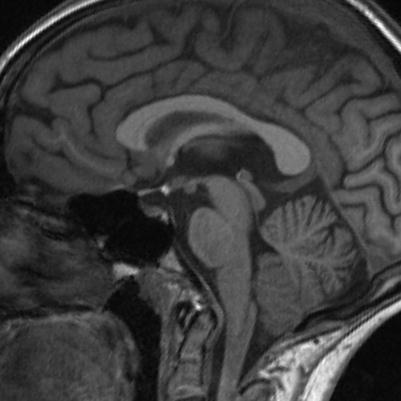

Fig. 68.2
Pituitary hypoplasia. Sagittal T1-weighted precontrast MR image. There is a T1-hyperintense spot in the infundibular recess, indicating ectopic neurohypophysis, and the pituitary stalk is not seen. The anterior pituitary gland is present in the sella
The presence of diabetes insipidus has been shown to correlate with loss of the posterior pituitary bright spot [23, 24].
Pituitary hypoplasia or ectopia can be associated with agenesis of an internal carotid artery [25, 26].
On MRI, the cross-sectional area of the optic nerve can be used to support the diagnosis of optic nerve hypoplasia [27].
68.3 Clinical Management
Clinical management is centered on prompt diagnosis and hormone replacement.
Favorable responses to GH replacement have been shown in many patients [28].
Multidisciplinary management is recommended for patients with any midline developmental disorders. Among the clinicians required may be endocrinologists, ophthalmologists, psychiatrists, neurologists, neurosurgeons, genetic counselors, and visual and occupational therapists.
References
1.
2.
Raivio T, Avbelj M, McCabe MJ, Romero CJ, Dwyer AA, Tommiska J, et al. Genetic overlap in Kallmann syndrome, combined pituitary hormone deficiency, and septo-optic dysplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:E694–9.PubMedCentralCrossRefPubMed
3.
4.
Baş F, Darendeliler F, Yapici Z, Gökalp S, Bundak R, Saka N, Günöz H. Worster-Drought syndrome (congenital bilateral perisylvian syndrome) with posterior pituitary ectopia, pituitary hypoplasia, empty sella and panhypopituitarism: a patient report. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2006;19:535–40.PubMed
5.
6.
Frisch H, Kim C, Häusler G, Pfäffle R. Combined pituitary hormone deficiency and pituitary hypoplasia due to a mutation of the Pit-1 gene. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2000;52:661–5.CrossRef
7.
Pfäffle RW, DiMattia GE, Parks JS, Brown MR, Wit JM, Jansen M, et al. Mutation of the POU-specific domain of Pit-1 and hypopituitarism without pituitary hypoplasia. Science. 1992;257:1118–21.CrossRefPubMed
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








