13 Psychiatry of sexuality
Introduction
Psychosexual disorders can be divided into disorders of sexual preference and disorders of sexual functioning. The forensic aspects of the former are addressed in Chapter 21.
Sexual response
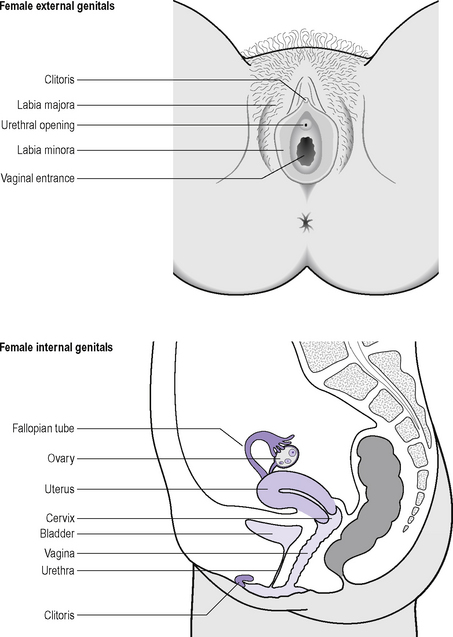
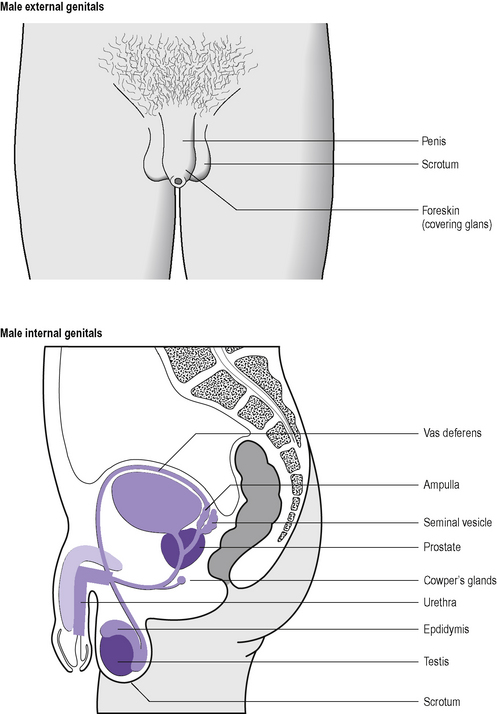
Before considering the sexual response it is important to be familiar with the anatomy of the human genitalia. The important structures are depicted in Figures 13.1 and 13.2. It must be remembered, however, that sexual responsiveness is not confined to the genitalia but can and does involve the whole body. Indeed, this is an important consideration in some of the treatments for sexual dysfunction.
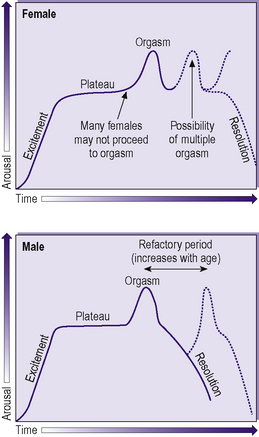
In Masters and Johnson’s model:
The relative timings of each of these phases are shown in Figure 13.3. In females there may be rapid response to reach orgasm (e.g. during masturbation). In either sex there may be excitement and plateau without orgasm, although this is much more common in the female. In males there is a refractory period after orgasm during which a further orgasm cannot occur. The length of this increases with age.
Classification and diagnosis of sexual disorders
The ICD-10 category for disorders of sexual preference is shown in Table 13.1 and the DSM-IV-TR category for paraphilias in Table 13.2. These may variously be referred to as paraphilias, perversions or sexual deviances, although the latter two labels have become regarded as stigmatizing in many circles, perhaps because of the overlap between these disorders and sexual offences (see Chapter 21). Disorders of sexual preference are characterized by sexually arousing fantasies, urges and/or activities, which are not part of normative sexual functioning and which interfere with reciprocal affectionate activity. Some of these activities are illegal, but this can vary between jurisdictions. Some of the activities, such as voyeurism and exhibitionism, can present to a lesser degree in ‘normal’ sexuality, but are not persistent or preferred. Mental illness may be associated with the disorder of sexuality and should be diagnosed if present.
Table 13.1 I CD-10 classification: F65 Disorders of sexual preference
| F65.0 Fetishism |
| Reliance on some non-living object as a stimulus for sexual arousal, e.g. articles of clothing, particular texture such as rubber or plastic |
| F65.1 Fetishistic transvestism |
| Wearing of opposite-sex clothes for sexual excitement |
| F65.2 Exhibitionism |
| Recurrent or persistent tendency to expose the genitalia to strangers (usually of the opposite sex) or to people in public places |
| F65.3 Voyeurism |
| Recurrent or persistent tendency to look at people engaging in sexual or intimate behaviour such as undressing |
| F65.4 Paedophilia |
| Sexual preference for children, usually prepubertal or early pubertal |
| F65.5 Sadomasochism |
| Preference for sexual activity that involves bondage or the infliction of pain or humiliation. Preference to be the recipient is masochism, to be provider is sadism |
| F65.6 Multiple disorders of sexual preference |
| Most common combination is fetishism, transvestism and sadomasochism |
| F65.7 Other disorders of sexual preference, e.g. |
| Frotteurism: rubbing up against people for sexual stimulation in crowded public places |
| Necrophilia: preference for sexual activity with corpses |
| Zoophilia: preference for sexual activity with animals (bestiality) |
| Scotophilia: arousal from viewing of sexual scenes and genitalia (as with viewing of pornography) |
| Telephone scatalogia: making of obscene telephone calls |
Table 13.2 DSM-IV-TR Paraphilias
| 302.40 Exhibitionism |
| 302.81 Fetishism |
| 302.89 Frotteurism |
| 302.20 Paedophilia |
| 302.83 Sexual masochism |
| 302.84 Sexual sadism |
| 302.3 Transvestic fetishism |
| 302.82 Voyeurism |
| 302.9 Paraphilia NOS |
NOS, not otherwise specified
The ICD-10 and DSM-IV-TR classifications of sexual dysfunction (Tables 13.3 and 13.4) refer to disorders of normal sexual functioning. Anxiety, depression and other psychiatric disorders, which all have an effect on sexual responsiveness, should be considered in assessing sexual dysfunction and diagnosed if appropriate. The anergia of schizophrenia can include a reduction in sexual drive.
Table 13.4 DSM-IV-TR classification of sexual dysfunctions
| Sexual desire disorders |
| 302.71 Hypoactive sexual desire disorder |
| 302.79 Sexual aversion disorder |
| Sexual arousal disorders |
| 302.72 Female sexual arousal disorder |
| 302.72 Male erectile disorder |
| Orgasmic disorders |
| 302.73 Female orgasmic disorder |
| 302.74 Male orgasmic disorder |
| 302.75 Premature ejaculation |
| Sexual pain disorders |
| 302.76 Dyspareunia (not due to a general medical condition) |
| 306.51 Vaginismus (not due to a general medical condition) |
Specifiers: lifelong type/acquired type; generalized type/situational type; due to psychological factors/due to combined factors
Disorders of sexual preference
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree