Fig. 15.1
Thyrotroph (TSH) adenoma. (a) Sagittal T1-weighted post-gadolinium image. (b) Coronal T1-weighted post-gadolinium image. A cystic, enhancing mass is present in the superior anterior part of the sella. There is no encasement of bilateral cavernous internal carotid arteries. The mass contacts the optic chiasm without significant displacement
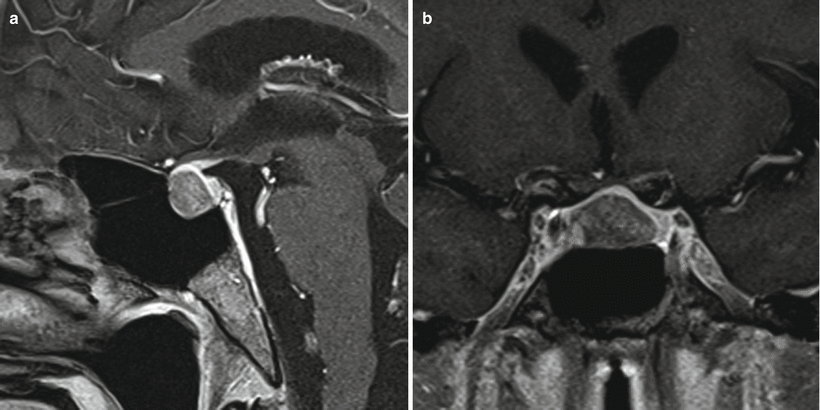
Fig. 15.2
TSH adenoma. (a) Sagittal T1-weighted post-gadolinium image. (b) Coronal T1-weighted post-gadolinium image. A hypoenhancing mass is located in the right aspect of the sella, contacting the right cavernous internal carotid artery without encasement. The mass contacts the optic chiasm without significant displacement
15.2.2 Histopathology
These tumors are differentiated via expression of thyrotroph embryonic factor (TEF) and GATA-2 transcription factors [10].
Histopathologically, medium-sized, elongated chromophobic cells are observed, with sinusoidal growth pattern, partial PAS immunoreactivity, and globular inclusions (Fig. 15.3) [2].
They frequently demonstrate immunoreactivity for TSH and the alpha-subunit [1].
These tumors have been reported to have a relatively high rate of atypical features [6].
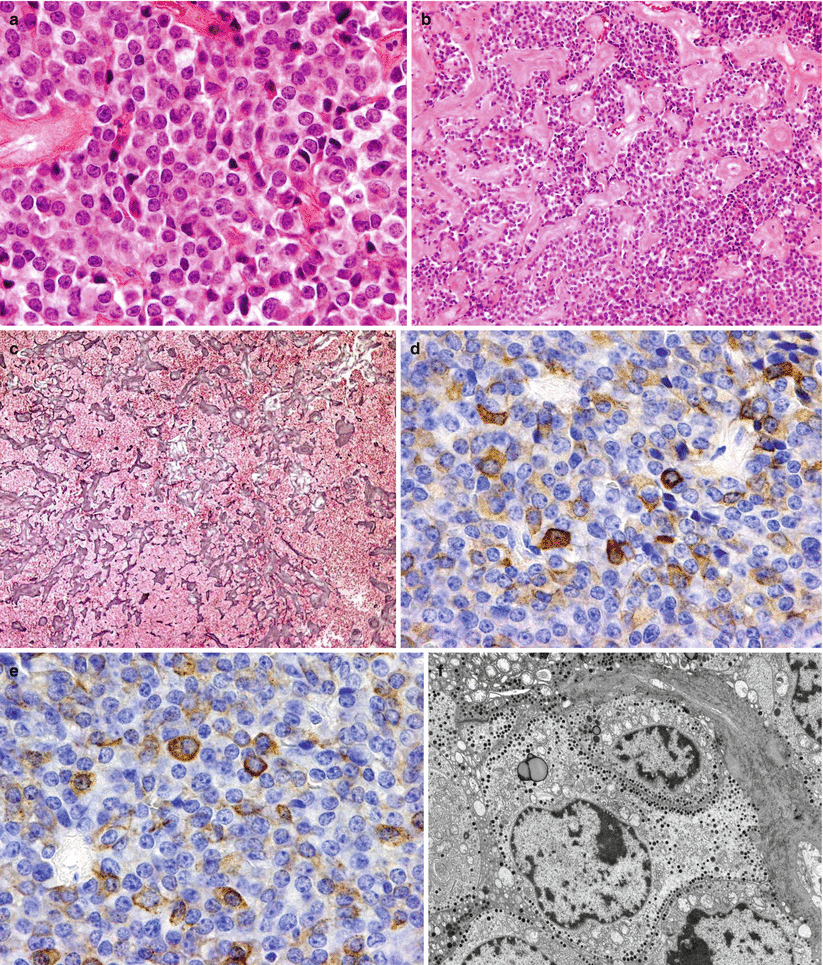
Fig. 15.3
TSH adenoma. (a) This TSH cell adenoma shows small to medium cells with chromophobic to acidophilic cytoplasm and central nuclei with delicate chromatin. Increased stromal fibrosis seen on H&E stain (b) and highlighted by reticulin staining (c) is commonly seen in these adenomas. Immunostains for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) may show variable intensity (d), and reactivity for the α-subunit of the glycoproteins (e) is commonly seen. The ultrastructure of thyrotroph cell adenomas shows angular cells with rich subcellular organelles and the presence of small, dense secretory granules displayed near the plasmalemma (f)
15.3 Clinical Management
For control of unresectable tumors, somatostatin analogues are effective in decreasing excess TSH secretion [11]. Pretreatment with octreotide has been reported to result in tumor shrinkage prior to surgical resection [9, 12].
Gross total resection with hormonal remission has been reported in approximately 50–60 % of patients—a rate that can be improved with adjunctive radiation or radiosurgery [1, 4, 9].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







