56
Thoracoplasty: Anterior, Posterior
Carrie A. Diulus and Isador H. Lieberman
Description
Thoracoplasty is a technique involving rib resection to alleviate the cosmetic rib deformity associated with scoliosis.
Expectations
Cosmetic improvement of truncal appearance.
Indications
Rib deformity is commonly encountered with advanced curves in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis or congenital scoliosis with or without a previous posterior fusion. It may be a sequela of crankshafting after a previous posterior fusion. Patients typically present with cosmetic concerns and coronal sitting imbalance. Indications include the following:
- Progressive or cosmetically unacceptable rib humps
- To balance shoulder heights
- To correct coronal sitting imbalance secondary to rib hump
- As a source of bone graft for both anterior and posterior fusion procedures
Contraindications
- Patients without a cosmetically noticeable rib deformity
- Patients who cannot tolerate the pulmonary compromise of a thoracoplasty due to poor compliance of the chest cage, resection of numerous ribs, division of accessory respiratory muscles, or detachment of the diaphragm
Special Considerations
To prevent reoccurrence, delay thoracoplasty until the patient is physiologically mature.
Special Instructions, Position, and Anesthesia
There are three techniques to perform a rib resection thoracoplasty: (1) open internal transthoracic, (2) open posterior single or double incision, and (3) endoscopic internal transthoracic. Each has its merits, and the technique used depends on the clinical circumstances. Each case should be judged on its individual merits and ultimate expectations.
Open Anterior Transthoracic Internal
- Selective double-lumen endotracheal intubation
- Lateral position
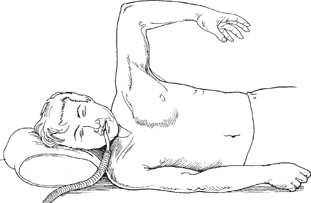
- Drape arm free to facilitate intraoperative evaluation of scapular position (Fig. 56.1)
- Drape from midline posteriorly to sternum anteriorly
Fig. 56.1 Operative positioning.
Open Posterior with Single Midline, or Midline and Posterior Axillary Line Incisions
- Prone position
- Drape field from one anterior axillary line to the opposite anterior axillary line
Endoscopic Transthoracic Internal
- Selective double-lumen endotracheal intubation
- Lateral position
- Drape arm free to facilitate intraoperative evaluation of the scapular position (Fig. 56.1)
- Drape from midline posteriorly to sternum anteriorly
Tips, Pearls, and Lessons Learned
- Trim rib flush with transverse process at each level to avoid scapular impingement with motion
- Thoracotomy instruments should be quickly available during endoscopic procedure for emergency open exposure
- To estimate the correction required, one must evaluate and record the extent and location of scoliotic curve, the flexibility of the structural and compensatory curves, coronal and sagittal balance, shoulder heights, and the extent of scapular winging. Evaluating the curve parameters allows the surgeon to decide if the spine, the ribs, or both need to be addressed. Documenting the shoulder heights and scapular winging establishes a benchmark to advise on expectations.
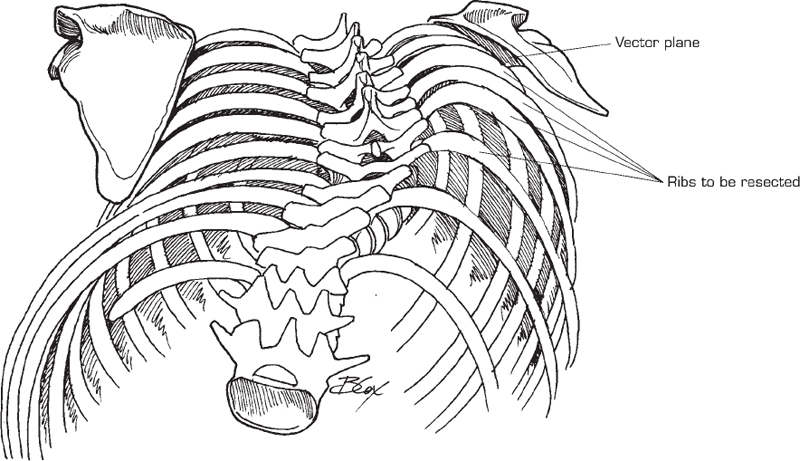
- Three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) reconstruction with vector plane analysis can help estimate the locations and the extent of ribs to be resected (this technique, by creating a virtual plane parallel to the left scapula and intersecting the right-sided rib deformity, allows for an estimate of which ribs, and their lengths, are to be resected). This resected amount allows the right scapula to descend into the resection bed to balance with the left side (Fig. 56.2).
- Pulmonary function tests to assess feasibility of single lung ventilation if thoracotomy or endoscopic approach is considered